Gabriele Stoll
Natural Crop Protection in the Tropics
Letting Information Come to Life
Insect pests in field and Storage
Diamondback moth (DBM)
Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera:
Plutellidae)
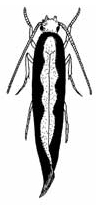
Diamondback moth: Adult
Host plants
Primary
Cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, rape
Secondary
Mustard and most of the wild crucifers
Distribution
Worldwide. It is a particularly important
pest in the lowlands in the tropics and subtropics.
Life cycle
The less than 1 mm, yellowish eggs are
laid preferably on the upper surface of the leaves, close to
the leaf veins, either singly or in small groups. After
3–8 days the pale green caterpillars hatch which grow to
about 12 mm long. When they are disturbed they wiggle away
quickly and drop from the leaf on a silken thread. If they
should fall from the leaf they remain hanging from it by a
silken thread from which they climb back once the danger has
passed. After 14–18 days they pupate inside a cocoon,
looking like a white silk mesh, attached to the underside of
the leaf. The colour of the pupa inside is green. After another
5–10 days tiny grey-brownish moths emerge which have a
wing span of only 15 mm. On the rear edge of each forewing are
3 pale triangular markings which form a diamond pattern when
the wings are folded. Moths are more active and visible at
dusk. They fly around plants searching for a mate or a place to
deposit eggs. Under favourable conditions up to 18 generations
per year are possible.
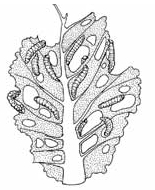
Larva on damaged leaf
Diamondback moth:
Larva
Damage pattern
The caterpillars feed primarily on the
leaves. They prefer the undersides and do not eat the veins.
Initial damage results in small incomplete holes caused by
young larvae and larger complete holes caused by mature larvae.
The entire plant may become riddled with holes under moderate
to heavy populations. Larvae also feed in the developing heads
of cabbage causing deformed heads and encouraging soft rots. It
is not uncommon that crucifer fields are completely destroyed
by this pest.
Control measures
Threshold level
When surveying small cabbage plots for
pest occurrence (0.25 ha) it is recommended to sample at least
60 plants. The action threshold is reached if, before head
formation of cabbage, 50% of the plants are infested with 5 or
more larvae per plant. After head formation it is 1 caterpillar
per plant.
Natural enemies
Parasitoids:
Eggs: Trichogramma
chilonis
Larvae: Diadegma (D. semiclausum, D.
insularis), Apanteles plutellae
Predators:
Ants, Polybia spp.
Pathogens:
Conidiobolus spp.
(Mycoinsecticide).
Management practices
• Avoid planting during the hot
season, particularly at the end of the dry season.
• Separate seedbed and field to
reduce danger of carrying over the pest from one site to the
other and to ensure infestation-free planting material.
• Monitor twice a week.
Cultural methods
• Cabbage seedlings should be
damage-free before transplanting to the field.
• Intercropping combined with the
application of neem seed kernel extract has been found to be
very effective.
• Intercropping cabbage-tomato and
the application of neem extracts has been found to be
comparable to that of the recommended insecticide.
• Planting marigold, Tagetes spp., as
a trap crop has given a 30–50% reduction of the larval
population.
• Cultivate bold-seeded Indian
mustard as trap crop. This attracts up to 80% of DBM, and
should be sown thickly all around the area where crucifers are
to be grown, at least 10 days before the cruciferous crops
themselves.
• Prunings of healthy tomato plants
can be scattered as a mulch in the cabbage field because of its
deterrent effect on the DBM.
• Unharvested plants and crop
residues are an important source of infestation. Remove and
destroy all the unharvested plants from the field as well as
alternate hosts and weed hosts (173).
• Ploughing the land over and leaving
it exposed to the hot sun at least one week before cultivation
helps to clean up sources of DBM.
Insect-controlling plants
• Annona spp.
• Chilli
• Derris (3)
• Mammea
americana
• Neem seed extracts
• Persian lilac
• Tephrosia
candida
• Turmeric
PRZYBYSEZEWSKI suggests spraying at
transplanting or within a few days afterwards in order to
prevent an early build-up of DBM populations. Thus damage can
be contained more effectively. The spraying liquid should be
directed on the underside of the foliage and inside the head
where the larvae live.
Other methods
• Bacillus
thuringiensis
• Yellow-sticky trap